Instead, we simply keep deducting depreciation until we reach the salvage value. The current year depreciation is the portion of a fixed asset’s cost that we deduct against current year profit and loss. The accounting concept behind depreciation is that an asset produces revenue over an estimated number of years; therefore, the cost of the asset should be deducted over those same estimated years. There are various alternative methods that can be used for calculating a company’s annual depreciation expense. Nevertheless, businesses should carefully evaluate their specific circumstances and asset types when choosing a depreciation method to ensure that it aligns with their financial objectives and regulatory requirements.
What Is a Suspense Account: Definition, Types and Examples
Thus, an increase in the cost of repairs of each subsequent year is compensated by a decrease in the amount of depreciation for each subsequent year. By contrast, the opposite is true when applying the straight-line method, the unit-of-production method, and the sum-of-the-years-digits method. LegalZoom provides access to independent attorneys and self-service tools. LegalZoom is not a law firm and does not provide legal advice, except where authorized through its subsidiary law firm LZ Legal Services, LLC. Use of our products and services is governed by our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.

Double Declining Balance Depreciation Example
Depreciation in the year of disposal if the asset is sold before its final year of useful life is therefore equal to Carrying Value × Depreciation% × Time Factor. No depreciation is charged following the year in which the asset is sold. It is important to note double declining balance method that we apply the depreciation rate on the full cost rather than the depreciable cost (cost minus salvage value). Therefore, it is more suited to depreciating assets with a higher degree of wear and tear, usage, or loss of value earlier in their lives.
Why would a company use double-declining depreciation on its financial statements?
- Get instant access to lessons taught by experienced private equity pros and bulge bracket investment bankers including financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel Modeling.
- Since it always charges a percentage on the base value, there will always be leftovers.
- 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas.
- By contrast, the opposite is true when applying the straight-line method, the unit-of-production method, and the sum-of-the-years-digits method.
- All information prepared on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be relied on for legal, tax or accounting advice.
It reflects the asset’s reduction in value due to wear and tear, obsolescence, or age. Depreciation helps businesses match expenses with revenues generated by the asset, ensuring accurate financial reporting. As an alternative to systematic allocation schemes, several declining balance methods for calculating depreciation expenses have been developed.
- The expense would be $270 in the first year, $189 in the second year, and $132 in the third year if an asset costing $1,000 with a salvage value of $100 and a 10-year life depreciates at 30% each year.
- This approach ensures that depreciation expense is directly tied to an asset’s production or usage levels.
- Enter the straight line depreciation rate in the double declining depreciation formula, along with the book value for this year.
- LegalZoom is not a law firm and does not provide legal advice, except where authorized through its subsidiary law firm LZ Legal Services, LLC.
- Increase your desired income on your desired schedule by using Taxfyle’s platform to pick up tax filing, consultation, and bookkeeping jobs.

Through this example, we can see how the DDB method allocates a larger depreciation expense in the early years and gradually reduces it over the asset’s useful life. This approach matches the higher usage and faster depreciation of the car in its initial years, providing a more accurate reflection of its value on the company’s financial statements. Depreciation is the process by which you decrease the value of your assets over their useful life. The most commonly used method of depreciation is straight-line; it is the simplest to calculate.
Calculating the Depreciation Formula for DDB
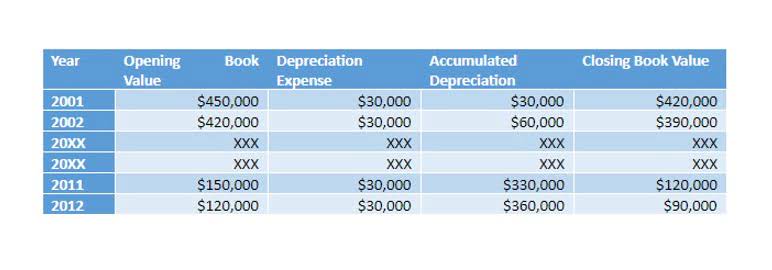
This is the fixture’s cost of $100,000 minus its accumulated depreciation of $36,000 ($20,000 + $16,000). The book value of $64,000 multiplied by 20% is $12,800 of depreciation expense for Year 3. At the beginning of the first year, the fixture’s book value is $100,000 since the fixtures have not yet had https://www.bookstime.com/ any depreciation. Therefore, under the double declining balance method the $100,000 of book value will be multiplied by 20% and will result in $20,000 of depreciation for Year 1. The journal entry will be a debit of $20,000 to Depreciation Expense and a credit of $20,000 to Accumulated Depreciation.